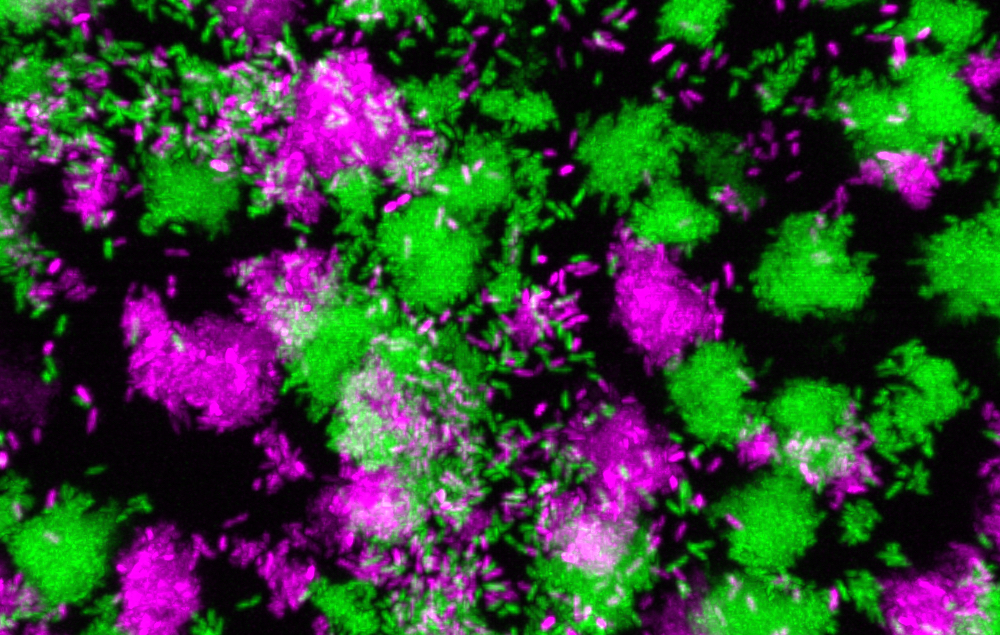
People with weakened immune systems are at constant risk of infection. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a common environmental bacterium, can colonize different body parts, such as the lungs, leading to persistent, chronic infections that can last a lifetime – a common occurrence for people with cystic fibrosis.
But the bacteria can sometimes change their behavior and enter the bloodstream, causing chronic localized infections to become acute and potentially fatal. Despite decades of studying the transition in lab environments, how and why the switch happens in humans has remained unknown.
Read the rest of the story here.
For More Information Contact
Catherine Barzler, Senior Research Writer/Editor